Research Research Highlights
Research Highlights
Research Highlights
Research Highlights
Research Highlights 미리보기

First to Uncover What Happens to mRNA Vaccines in the Body
Prof. V. Narry Kim
A Korean research team has, for the first time globally, elucidated the intracellular mechanisms by which mRNA vaccines function, marking a significant advancement in RNA-based therapeutics.
Research Highlights Board
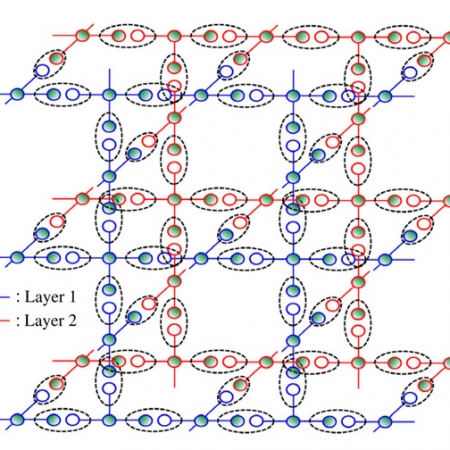
Resource-Efficient Topological Fault-Tolerant Quantum Computation with Hybrid Entanglement of Light
Prof. Hyunseok Jeong
We propose an all-linear-optical scheme to ballistically generate a cluster state for measurement-based topological fault-tolerant quantum computation using hybrid photonic qubits entangled in a continuous-discrete domain.
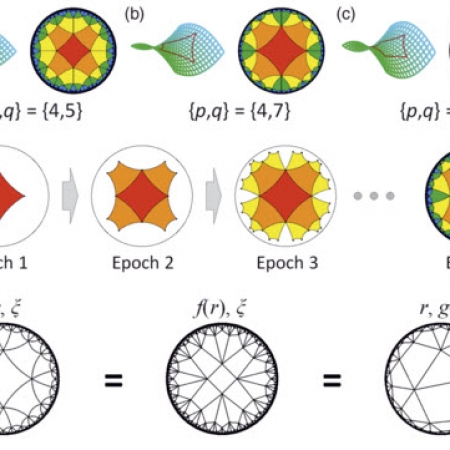
Topological Hyperbolic Lattices
Prof. Namkyoo Park
Non-Euclidean geometry, discovered by negating Euclid’s parallel postulate, has been of considerable interest in mathematics and related fields for the description of geographical coordinates, Internet infrastructures, and the general theory of relativity.
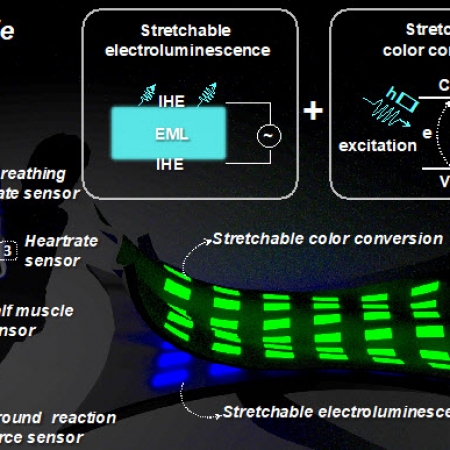
Water Passivation of Perovskite Nanocrystals Enables Air‐Stable Intrinsically Stretchable Color‐Conversion Layers for Stretchable Displays
Prof. Tae-Woo Lee
Conventional organic light‐emitting devices without an encapsulation layer are susceptible to degradation when exposed to air, so realization of air‐stable intrinsically‐stretchable display is a great challenge because the protection of the devices against penetration of moisture and oxygen is even more difficult under stretching.
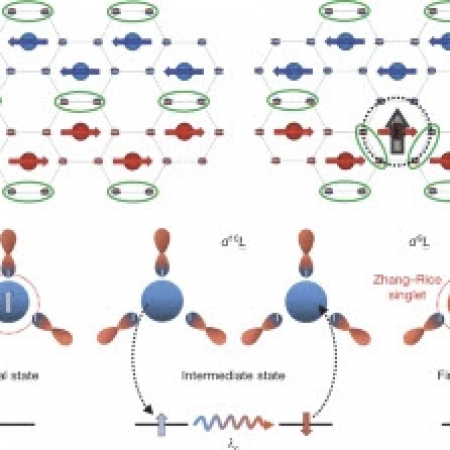
Coherent many-body exciton in van der Waals antiferromagnet NiPS3
Prof. Je-Geun Park
An exciton is the bosonic quasiparticle of electron–hole pairs bound by the Coulomb interaction. Bose–Einstein condensation of this exciton state has long been the subject of speculation in various model systems, and examples have been found more recently in optical lattices and two-dimensional materials.

Ionic spiderwebs enable cleaning contamination on itself, sensing approaching targets, capturing and releasing those targets
Prof. Ho-young Kim, Prof. Jeong Yun Sun
Spiders use adhesive, stretchable, and translucent webs to capture their prey. However, sustaining the capturing capability of these webs can be challenging because the webs inevitably invite contamination, thus reducing its adhesion force. To overcome these challenges, spiders have developed strategies of using webs t...
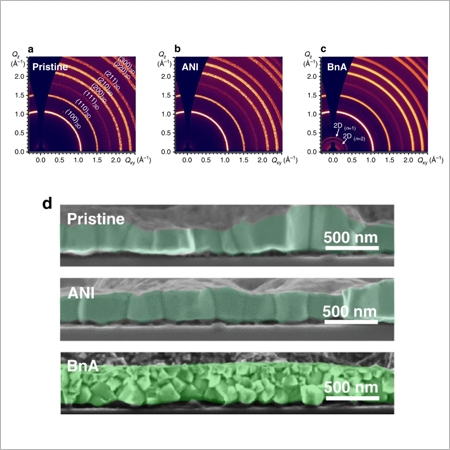
Proton-transfer-induced 3D/2D hybrid perovskites suppress ion migration and reduce luminance overshoot
Prof. Tae-Woo Lee, Department of Materials Science and Engineering
Perovskite light-emitting diodes (PeLEDs) based on three-dimensional (3D) polycrystalline perovskites suffer from ion migration, which causes overshoot of luminance over time during operation and reduces its operational lifetime. Here, we demonstrate 3D/2D hybrid PeLEDs with extremely reduced luminance overshoot and 21...
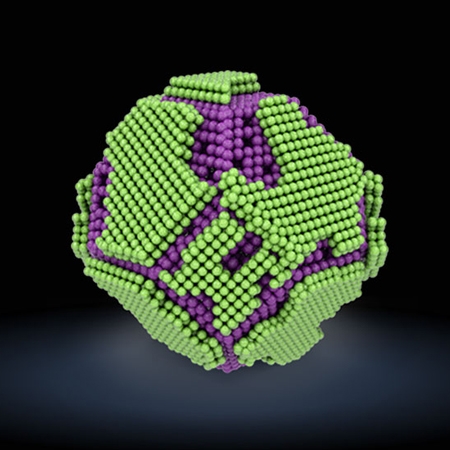
Epitaxially Strained CeO2/Mn3O4 Nanocrystals as an Enhanced Antioxidant for Radioprotection
Prof. Taeghwan Hyeon, Prof. Kyungpyo Park
Nanomaterials with antioxidant properties are promising for treating reactive oxygen species (ROS)-related diseases. However, maintaining efficacy at low doses to minimize toxicity is a critical for clinical applications.
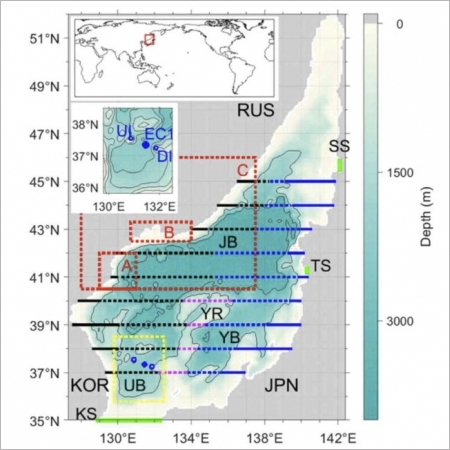
Decadal Changes in Meridional Overturning Circulation in the East Sea (Sea of Japan)
Prof. SUNGHYUN NAM
Meridional overturning circulation (MOC) is vital to distributing heat, freshwater, and dissolved matter in semienclosed deep marginal seas such as the East Sea (ES) (Sea of Japan). As our understanding of the ES MOC remains incomplete, we attempted to fill this research gap. We analyzed the ES MOC and its decadal chan...
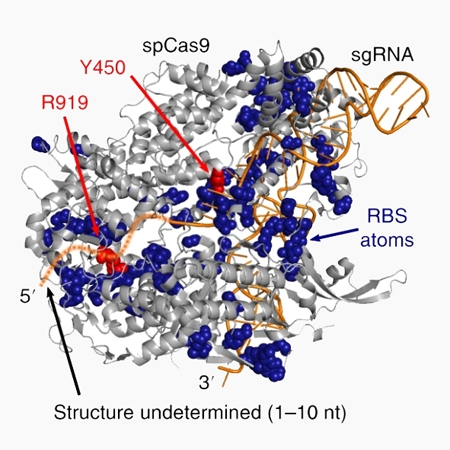
Chemical RNA digestion enables robust RNA-binding site mapping at single amino acid resolution
School of Biological Sciences V. Narry Kim, Jong-Seo Kim
Abstract RNA-binding sites (RBSs) can be identified by liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry analyses of the protein–RNA conjugates created by crosslinking, but RBS mapping remains highly challenging due to the complexity of the formed RNA adducts. Here, we introduce RBS-ID, a method that uses hydrofluorid...
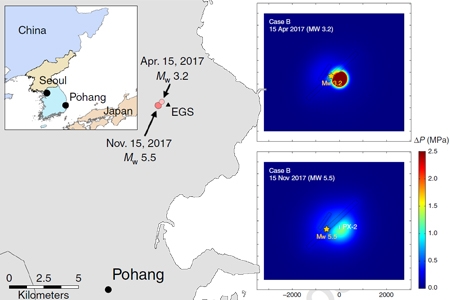
Causal mechanism of injection-induced earthquakes through the Mw 5.5 Pohang earthquake case study
Prof. Lee, KangKun, School of Earth and Environmental Sciences
Causal mechanisms for fluid injection-induced earthquakes remain a challenge to identify. Past studies largely established spatiotemporal correlations. Here, we propose a multi-process causal mechanism for injection-induced earthquakes through a case study of the 2017 Mw 5.5 induced earthquake near Pohang Enhanced Geot...
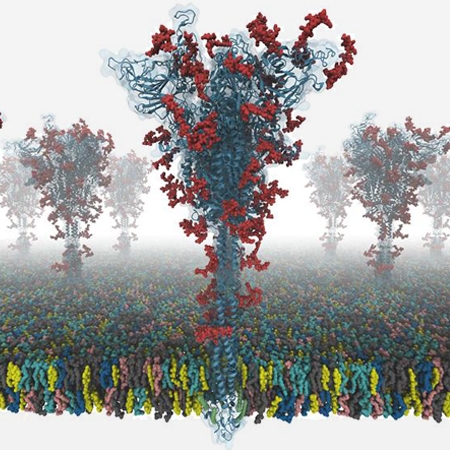
Modeling and Simulation of a Fully-glycosylated Full-length SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein in a Viral Membrane
Prof. Chaok Seok
This technical study describes all-atom modeling and simulation of a fully-glycosylated fulllength SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) protein in a viral membrane. First, starting from PDB:6VSB and 6VXX, full-length S protein structures were modeled using template-based modeling, de-novo protein structure prediction, and loop modelin...


